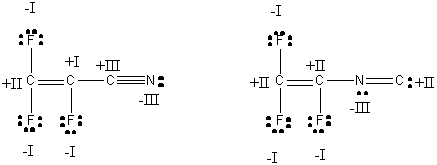
| bond | typical bond length (Å) |
| C=C |
|
| C=C |
|
| C=N |
|
| C=N |
|
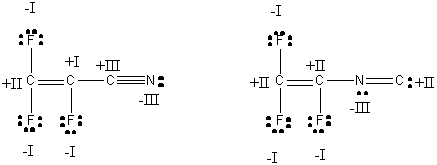
All formal charges are 0 and oxidation numbers are as shown.
The electronegative F atom will withdraw some of the electron density from the double bonds, causing them to lengthen a bit, so the C=C length in each isomer will be ~ 1.2 Å. The C-F bonds should be fairly typical, ~1.38 Å. In the nitrile isomer (left), the C-C bond is shortened a bit by conjugation to ~1.5 Å and the nitrile bond lengthened a bit to ~1.15-1.16 Å. In the isonitrile isomer (right), conjugation should shorten the C-N bond to ~1.45 Å and lengthen the N=C bond to ~ 1.3 Å. The CF2 and CF centers in both isomers are sp2 hybridized with 120o bond angles. The nitrile C in the left isomer is sp hybridized with a 180o bond angle while the isonitrile N in the right isomer is sp2 hybridized with a bond angle reduced from the ideal 120o to ~116o.