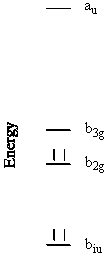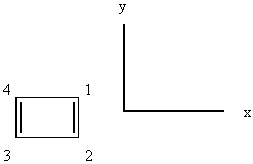
1. Cyclobutadiene, shown below, is an antiaromatic molecule
(that is, the π electrons do not delocalize
around the ring). In this problem you will construct the molecular orbital
diagram for the π system by considering each
π
orbital as a group orbital on the carbon atoms. Use the axis system shown
(z is perpendicular to the page) and the pz orbitals on each
carbon atom as the basis set. Find the irreducible representations of the
π orbitals. Use the projection operator technique
to find the wavefunctions of each of the π orbitals.
Sketch each of these orbitals. Energy order the orbitals and show the electron
occupation in your MO diagram.

Number the C atoms. Cyclobutadiene belongs to
the D2h point group:
| D2h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ag |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x2, y2, z2 | |
| b1g |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rz | xy |
| b2g |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ry | xz |
| b3g |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rx | yz |
| au |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
| b1u |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
z | |
| b2u |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y | |
| b3u |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
Total representation for the π
orbitals:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| pz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This reduces to b2g + b3g + au + b1u
Rotation operator:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rp1z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Projection operator:
P(b2g) = p1z - p3z - p4z + p2z - p3z + p1z + p2z - p4z
![]()
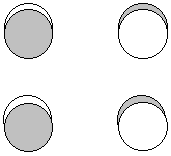
1 node between the sigma (long) bonds
P(b3g) = p1z - p3z + p4z - p2z - p3z + p1z - p2z + p4z
![]()
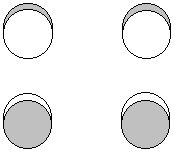
1 node between the pi (short) bonds
P(au) = p1z + p3z - p4z - p2z + p3z + p1z - p2z - p4z
![]()
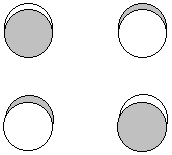
2 nodes
P(b1u) = p1z + p3z + p4z + p2z + p3z + p1z + p2z + p4z
![]()
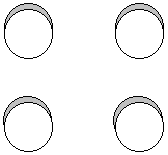
0 nodes
Energy Level Diagram: