Chemistry 401
Intermediate Inorganic Chemistry
University of Rhode Island
Fall 2017
Final Exam
All citations are to Inorg. Chem., 2017, 56
1. R. T. P. Sant’Anna and R. B. Faria (pages 11160 – 11167) investigated the kinetics of the reaction between chlorate and nitrous acid under acidic conditions. Balance the reaction shown below. Use the Latimer diagrams given to estimate the standard potential for the reaction.
ClO3–(aq) + HNO2(aq) → Cl–(aq) + NO3–(aq)
NO3– → +0.803 N2O4 → +1.07 HNO2
ClO3– → +1.468 Cl2 → +1.358 Cl–
2. V. Yempally, S. Moncho, F. Hasanayn, W. Y. Fan, E. N. Brothers, and A. A. Bengali (pages 11244 – 11253) examined the photochemistry of Mn(bpy)(CO)3Br. Name each isomer of the compound, estimate the LFSE in terms of Dq and P, predict the stability of the compound using the EAN rule, and predict the distortion of the compound if it is Jahn-Teller active.
3. G. Ciancaleoni, L. Belpassi, and F. Marchetti (pages 11266 – 11274) address the debate whether chloride ion can back donate electron density into d orbitals in Nb(V). If this bonding motif can be achieved, which orbital(s) on the Cl– and which orbital(s) on the metal would be involved? Draw a sketch of the atomic orbitals that would be used to form the molecular orbital that would be involved in the back-donation.
4. Md. M. Rahman, M. D. Smith, J. A. Amaya, T. M. Makris, and D. V. Peryshkov (pages 11798 – 11803) used a Lewis pair, TaCl5-PPh3 (Ph = phenyl), to activate C-H bonds. Identify the Lewis acid, the Lewis base, and draw the structures and give the point group of each component.
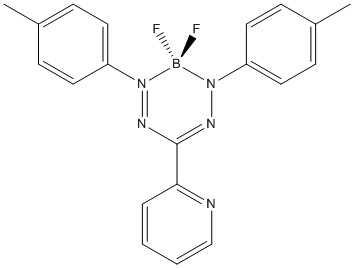
5. S. M. Barbon, J. V. Buddingh, R. R. Maar, and J. B. Gilroy (pages 12003 – 12011) studied the reactivity of the boron difluoride formazanate shown below. Give the formal charges for each B, F, and N atom. The compound is a Brønsted-Lowry base – which atom would act as the hydrogen-ion acceptor? Explain your reasoning.
6. M. A. Manumpil, C. Leal-Cervantes, M. R. Hudson, C. M. Brown, and H. I. Karunadasa (pages 12682 – 12686) synthesized a prussian blue analogue that contained vanadium species. Upon exposure to humid air the following reaction was observed: VO2+ + O2 → VO2+. Balance the reaction.
7. N. Das, S. Singh, A. G. Joshi, M. Thirumal, V. R. Reddy, L. C. Gupta, and A. K. Ganguli (pages 12712 – 12718) demonstrated that Pr2FeCoO6 has both a magnetic moment and an electric moment. Give the electron configuration of each ion in this compound.
8. M. A. Zykin, K. A. Babeshkin, O. V. Magdysyuk, E. O. Anokhin, W. Schnelle, C. Felser, M. Jansen, and P. E. Kazin (pages 14077 – 14083) doped cobalt into hydroxyapatite to create a magnetic material. Structural studies showed that the cobalt ligated by two oxide ions in an unusual bent geometry, [CoO2]2–. Predict the spin-only magnetic moment for the cobalt in units of Bohr-magnetons (recall: μ = [n(n+2)]½ μB). Explain how you made your decision to determine if the cobalt is in a high spin or low spin state.
9. R. K. Hona, A. Huq, and F. Ramezanipour (pages 14494 – 14505) investigated Ca2FeCoO6-δ. For δ = 0, give the likely oxidation state for each atom in the compound. When 0 < δ < 1, the compound is a semiconductor: is this p-type or n-type? Explain your reasoning.
10. J.-H. Feng, C.-L. Hu, H.-P. Xia, F. Kong, and J.-G. Mao (pages 14697 – 14705) studied the optical properties of Li7(TeO3)3F. Draw the Lewis structure for the TeO32– anion, predict the molecular structure, and estimate the bond angles to ±2°.