Chemistry 401
Intermediate Inorganic Chemistry
University of Rhode Island
Fall 2012
Final Exam
All references are to volume 51 of Inorganic Chemistry (2012).
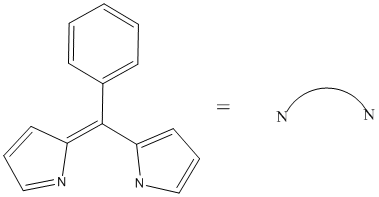
1. D. 1. McLean, Moody, Waterland, and Telfer (pages 446 – 455) reported the first dipyrrinato complexes of Re(I), fac-[ReL(CO)3Cl]–, where the dipyrrinato ligand is shown below. Draw the structure of this complex (use the abbreviation when drawing the structure), indicate if it is expected to be stable (explain your reasoning), give the point group, and predict the spin-only magnetic moment in units of Bohr-Magnetons.
2. Rayson, Mackie, Kennedy, and Dlugogorski (pages 2178 – 2185) studied the decomposition of nitrous acid, HNO2. The products of the decomposition are nitric oxide (NO), nitrate ion, hydrogen ion, and water. Write the balanced reaction.
3. Jackson, Dixon, and Christie (pages 2472 – 2485) calculated the thermodynamic properties of a number of selenium fluorides and selenium oxyfluorides. Write the Lewis structures for SeF4 and SeOF2, predict all of the bond angles, give the formal charge for each atom, give the oxidation number for each atom, and give the point group for each structure.
4. Li, Gai, Li, Wang, Niu, He, and Yang (pages 3963 – 3971) synthesized a number of lanthanide fluorides, LnF3. Consider LaF3, EuF3, and DyF3 and give the ground state term symbol for the metal ion in each compound.
5. Malliakis, Yao, Wells, Jin, Skanthakumar, Choi, Balasubramanian, Soderholm, Ellis, Kanatzidis, and Ibers (pages 6153 – 6163) investigated K6Cu12U2S15, which they found to be a semiconductor. The magnetic moment for the compound was observed to be quite low. Determine the likely oxidation state of the U in this compound. Give an explanation why this compound is a semiconductor.
6. Biswas, Patra, Maity, Ke, Adhikary, and Ghosh (pages 6687 – 6699) used mer-carbonylchlorohydridotris(triphenylphosphine)ruthenium(II) to react with 9,10-phenanthrene-quinone. Write the structure of the metal complex, give the point group, and determine the ligand field stabilization energy in terms of Dq and P.
7. Nolan, Amberger, Esselman, Thimmakondu, Stanton, Woods, and McMahon (pages 9846 – 9851) describe a simple synthesis of carbonyl azide OC(N3)2. Write the Lewis structure for this molecule, give the formal charges, and estimate all bond angles.
8. Lin, Chiou, Liu, Hsieh, Yu, and Liaw (pages 10092 – 10094) describe the tetranitrosylferrate(–I) anion. Predict the structure of this ion, give the point group, and determine if it is likely to be stable or not. Explain your reasoning.
9. Ali, Nuss, Kremer, and Jansen (pages 12336 – 12342) determined the structure of CsCoO2, which they considered novel because the cobalt ion occupies tetrahedral holes. Why would it be expected that the cobalt ion should reside in octahedral holes rather than tetrahedral holes? Explain your reasoning. (Hint: use LFSE as a guide.)
10. Malcolm, Sabourin, McDonald, Ferguson, and Rivard (pages 12905 – 12916) studied ammonia borane (H3NBH3) because this compound may have use for hydrogen storage applications. The problem with ammonia borane is that it readily polymerizes so the authors suggested using a Lewis acid and a Lewis base to stabilize the material. They chose to react ammonia borane with borane tetrahydrofuran and pyridine to test the hypothesis. Predict the structure of the product containing the ammonia borane fragment.