Chemistry 401
Intermediate Inorganic Chemistry
University of Rhode Island
Fall 2012
Exam 1
1. Find the electron configuration and ground state term symbol for a) Cu; b) Ni2+; c) Al3+; d) Ce+. Use the rare gas notation for closed shells.
a) Cu
[Ar]4s13d10
Only the 4s electron contributes to the term symbol: L = 0 and S = ½ giving 2S
b) Ni2+
[Ar]3d8
↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ so L = 3 and S = 1 giving 3F
+2 +1 0 –1 –2
c) Al3+
[Ne]
This is a closed shell so L = 0 and S = 0 giving 1S
d) Ce+
[Xe]4f3
↑ ↑ ↑ so L = 6 and S = 3/2 giving 4I
+3 +2 +1 0 –1 –2 –3
2. Write the Lewis dot structure showing the formal charges, predict the structure including an estimate of all bond angles, and indicate the likely hybrid orbital on the central atom for the following: a) SO3; b) XeO44–; c) IF3.
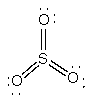
a) SO3
Lewis Structure:
Formal charges: S, 0; all three O, 0
Structure: trigonal planar with bond angles O-S-O 120°
Hybrid orbital on S: sp2
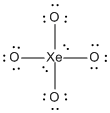
b) XeO44–
Lewis Structure:
Formal charges: Xe, 0; O, –1
Structure: square planar with bond angles O-Xe-O, 90°
Hybrid orbital on Xe: d2sp3
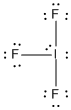
c) IF3
Lewis Structure:
Formal charges: I, 0; F , 0
Structure: bent T shaped with bond angles: F-I-F, ~89° and ~182°
Hybrid orbital on I: dsp3
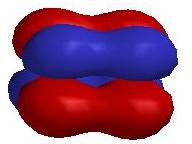
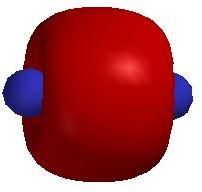
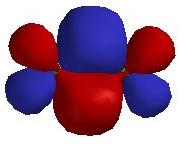
3. Several of the highest occupied molecular orbitals for Cr2 are shown below. Label the type of orbital and explain how you reached that conclusion. Predict the energy ordering of these orbitals and explain your reasoning.
a)
b)
c)
d)
a)
The orbital has 2 nodes parallel to the internuclear axis and 1 node perpendicular to the internuclear axis, which indicates that this is a δ* orbital.
b)
The orbital has 2 nodes parallel to the internuclear axis and 0 nodes perpendicular to the internuclear axis, which indicates that this is a δ orbital.
c)
The orbital has 0 nodes parallel to the internuclear axis and 0 nodes perpendicular to the internuclear axis, which indicates that this is a σ orbital.
d)
The orbital has 1 node parallel to the internuclear axis and 0 nodes perpendicular to the internuclear axis, which indicates that this is a π orbital.
The likely energy ordering is σ (lowest energy) < π < δ < δ* (highest energy). This conclusion is based on the nodal properties, which indicate the amount of electron density between nuclei: fewer nodes means more nuclear screening and less nuclear-nuclear repulsion.
4. The Pauling electronegativity for Xe is estimated to be 2.60, about the same as S, which has χ = 2.58. Based on this, make a predictive comparison of the chemical reactivity of the two elements. Explain your reasoning. Possible useful information: IP1(S) = 10.360 eV; IP1(Xe) = 12.130 eV.
Based on the electronegativities it can be predicted that S and Xe would have similar chemical behavior. There is some experimental support for this: both form a neutral trioxide (SO3 and XeO3), an anionic tetraoxide (SO42– and XeO44–), and difluorides (SF2 and XeF2). The differences between the two are substantial, though. The S based compounds are more stable and Xe based compounds quite reactive. S also readily bonds to C and N while Xe does not.