Chemistry 401
Intermediate Inorganic Chemistry
University of Rhode Island
Fall 2011
Final Exam
All references are to Inorganic Chemistry, 50, 2011
1. D. Schnaars, G. Wu, and T. Hayton (pages 9642 - 9649) studied uranium chemistry. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of uranium trioxide with triflic acid. Possibly useful information: the uranyl ion, UO22+, has a bond energy larger than CO2; triflic acid, CH3SO3H, written HOTf, is a super acid with pKa ~ –15.
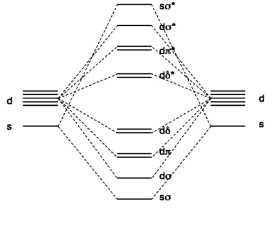
2. F. Ruipérez, J. Ugalde, and I. Infante (pages 9219 - 9229) determined the MO diagram for CrW(g), shown below. What basis set was used? What is the electron configuration? What is the bond order? Estimate the magnetic moment in units of Bohr-Magnetons. (Figure taken from Inorg. Chem., 2011, 50, 9219.).
3. Q. Yao and S. Brock (pages 9985 - 9992) used different ligands to influence the size of CdTe quantum dots. CdTe is a semiconductor with a size dependent band gap when the particle diameter is in the nm range as determined by emission spectroscopy. Using an appropriate bonding theory, explain why the size of the particle (at these small sizes) affects the band gap.
4. X. Zeng, E. Bernhardt, H. Beckers, and H. Willner (pages 11235 - 11241) investigated phosphorous azides. Predict all bond angles of OP(N3)3 using the Lewis structure.
5. R. Tan and D. Song (pages 10614 - 10622) synthesized complexes PtL(CH3)3+, where L is a bidentate neutral aromatic nitrogen donor. Do you expect this 5-coordinate complex to be stable? Why or why not?
6. B. Radaram, J. Ivie, W. Singh, R. Grudzien, J. Reibenspies, C. Webster, and X. Zhao (pages 10564 - 10571) studied water oxidation chemistry using ruthenium catalysts. Balance the reaction: H2O(l) + Ce4+(aq) → O2(g) + H+(aq) + Ce3+(aq) and estimate the standard potential. The reaction is catalyzed by a Ru2+ complex of general structure RuL1L2(H2O) where L1 is tridentate and L2 is bidentate. Is the activated complex inner sphere or outer sphere? Explain why.
7. M. Marszalek, Z. Fei, D.-R. Zhu, R. Scopelliti, P. Dyson, S. Zakeeruddin, and M. Grätzel (pages 11561 - 11567) analyzed the use of ionic liquids containing tricyanomethanide [C(CN)3]– or tetracyanoborate [B(CN)4]– anions in dye-sensitized solar cells. Draw the Lewis structures and estimate the bond angles for the anions. Ionic liquids have melting points less than 100 °C and typically use imidazolium derivatives as cations. What structural features of the anion and cation are responsible for a low enough lattice energy for a salt to be liquid at or near room temperature?
8. Z. Xue, J.-C. Daran, Y. Champouret, and R. Poli (pages 11543 - 11551) used 1H NMR spectroscopy to determine the solution structure of Fe(acac)2pyr2 (pyr = pyridine and acac = CH3(C=O)CH(C=O)CH3–), which is paramagnetic. Give the point group, LFSE, and magnetic moment for the two isomers.
9. T. Brewster, W. Ding, N. Schley, N. Hazari, V. Batista, and R. Crabtree (pages 11938 - 11946) reported single crystal x-ray structures for the two linkage isomers of the thiocyanate ligand bound to a Ru2+ complex. For the N bound isomer the Ru-N-C angle is 175.7° and the bond lengths are N-C 119 pm and C-S 161.3 pm. When S is bound to the metal the Ru-S-C angle is 106.7° and the bond lengths are N-C 113.3 pm and C-S 164.0 pm. Provide an explanation for these observations.
10. J. Schneider, K. Vuong, J. Calladine, X.-Z. Sun, A. Whitwood, M. George, and R. Perutz (pages 11877 - 11889) studied photochemistry of Re complexes. Draw the structure for fac-(bipyridine)tricarbonylpicolinerhenium(I) (picoline = 3-methylpyridine) and give the point group. This complex is used for the photoreduction of CO2 to CO - give the balanced half reaction for this reduction under acidic conditions.