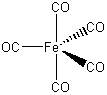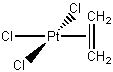Chemistry 401
Valence Bond Theory
Effective Atomic Number Rule (EAN): complexes with 18 (sometimes 16) electrons are stable (analogous to octet rule for main group elements)
Count the metal valence electrons and the electrons donated by the ligands; if this adds up to 18 (or 16), then the complex is predicted to be stable
EAN is most effective for low oxidation states and organometallic complexes
Organometallic complex: a compound with a metal to carbon bond.
Unlike the main group, d orbital lone pairs are generally not stereochemically active so the geometries of these compounds normally are determined solely by the number of ligands.
Examples
Fe(CO)5
Fe d8 (Note: when in a bonding situation, all of the electrons on a metal move to the orbital with the lowest n quantum number, similar to when ionization happens.)
CO 5(2) = 10
8 + 10 = 18
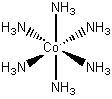
[Co(NH3)6]3+
Co d6
:NH3 6(2) = 12
6 + 12 = 18
Fe(cp)2
Fe2+ d6
cp– 2(6) = 12
6 + 12 = 18
Co(cp)2
Co2+ d7
cp– 2(6) = 12
7 + 12 = 19 not stable but Co(cp)2+ is stable
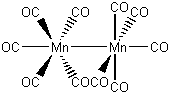
Mn2(CO)10
on each Mn: Mn d7
CO 5(2) = 10
M-M bond, 1
7 + 10 + 1 = 18
[PtCl3(CH2=CH2)]–
Pt2+ d8
Cl– 3(2) = 6
C2H4, 2
8 + 6 + 2 = 16