 Final Exam, Spring 2006
Final Exam, Spring 2006 Final Exam, Spring 2006
Final Exam, Spring 20061. Complete and balance the following chemical equations.
a. aqueous nitric acid plus aqueous cesium hydroxide
b. aqueous dihydrogen phosphate ion plus aqueous carbonate ion
c. aqueous sulfite ion plus water
d. H2SO4(aq) + Al(OH)3(s)
e. Co2+(aq) + NH3(aq)
f. H2SO4(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq)
g. Cr3+(aq) + PO43–(aq)
h. HCN(aq) + BrO3–(aq) → Br2(l) + C2N2(g)
i. Mg(s) + BrO–(aq) → Mg(OH)2(s) + Br2(l)
j. [AuCl4]–(aq) + Hg(l) → Hg22+(aq) + Au(s) + Cl–(aq)
2. For each of the following solutions or mixtures, list all of the dissolved ions and/or molecular species (except water) in the solution. Find the concentration of each of these species. Write the reactions that are needed to answer the question.
a. 0.1 M perchloric acid
b. 0.1 M potassium hydroxide
c. 0.1 M H2SO3
d. 0.1 M Cr(NO3)3
e. 0.1 mol BaF2 placed in 1 L of water
3. The rate constants for a reaction were measured and plotted as shown below:
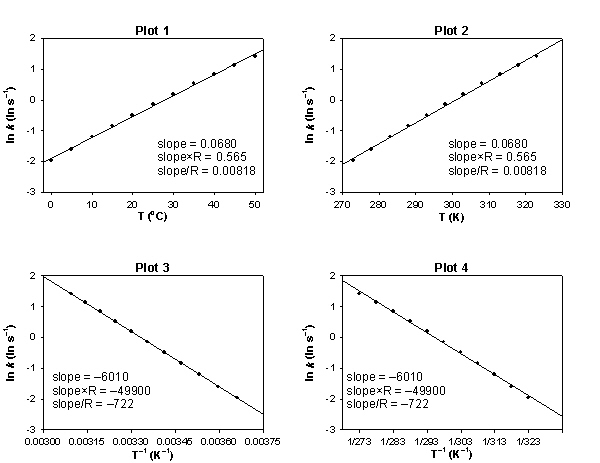
a. Which plot is correct to determine the activation energy? Why?
b. What is the value of the activation energy in units of kJ/mol?
c. What is the order of the reaction that was studied?
4. One of the homework assignments considered the following reaction:
MnO42–(aq) + O2(g) → MnO4–(aq) + H2O2(aq)
This series of questions will examine several different ways of obtaining ΔG°.
a. Balance the reaction under acidic conditions.
b. Find the standard potential under acidic conditions.
c. Use the standard potential to calculate ΔG° in units of kJ/mol.
d. Calculate ΔG° for the reaction in units of kJ/mol using the Gibb's energies of formation.
e. Calculate ΔH° for the reaction in units of kJ/mol.
f. Calculate ΔS° for the reaction in units of J/mol·K.
g. Use ΔH° and ΔS° to calculate ΔG° for the reaction in units of kJ/mol at 25 °C.
h. Consider the van't Hoff plot shown below for the reaction.
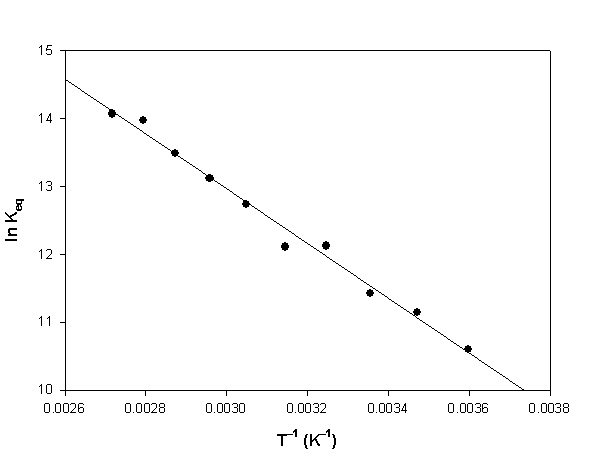
The following values were extracted from the plot: slope = –4030 and intercept = 25.1. What is the value for the enthalpy change for the reaction in units of kJ/mol? What is the value for the entropy change for the reaction in units of J/mol·K?
i. Calculate the value for the Gibb's energy change at 25 °C in units of kJ/mol using the van't Hoff plot data.
j. Compare all four values found for ΔG° and comment on any sources of error.
k. Is the reaction spontaneous or nonspontaneous? Which thermodynamic quantity is the controlling factor in the spontaneity - the enthalpy change or the entropy change?
5. Briefly answer the following questions:
a. One of the substances listed in the Table of Solubility Product Constants is bismuthyl hydroxide, BiOOH. Describe a simple test that confirms that this substance is (BiO)(OH), not Bi(OOH).
b. A solution is prepared that has pH = 4. Is this a strong acid or a weak acid?
c. Ka for the hydrolysis of Fe3+ is about ten million times larger than Ka for the hydrolysis of Fe2+. Explain why.