 Exam 2B, Spring 2002
Exam 2B, Spring 2002 Exam 2B, Spring 2002
Exam 2B, Spring 20021. Complete and balance the following acid/base reactions. Label the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base for each reaction.
a. aqueous perchloric acid plus solid magnesium hydroxide
b. aqueous nitric acid plus water
c. HBr(aq) + CN–(aq)
d. HClO3(aq) + H2O(l)
a. Mg(OH)2(s) + 2 HClO4(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 ClO4–(aq)
Acid: HClO4
Base: Mg(OH)2
Conjugate Acid: H2O
Conjugate Base: ClO4–
b. HNO3(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + NO3–(aq)
Acid: HNO3
Base: H2O
Conjugate Acid: H3O+
Conjugate Base: NO3–
c. HBr(aq) + CN–(aq) → HCN(aq) + Br–(aq)
Acid: HBr
Base: CN–
Conjugate Acid: HCN
Conjugate Base: Br–
d. HClO3(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + ClO3–(aq)
Acid: HClO3
Base: H2O
Conjugate Acid: H3O+
Conjugate Base: ClO3–
2. Write the chemical reaction needed to determine the pH and give the pH for the following solutions.
a. 0.0010 M hydroiodic acid.
b. 0.0010 M calcium hydroxide
a. 0.0010 M hydroiodic acid.
HI(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + I–(aq)
[H3O+] = [HI] = 0.0010 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log[0.0010] = 3.00
b. 0.0010 M calcium hydroxide
Ca(OH)2(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + 2 OH–(aq)
[OH–] = 2×[Ca(OH)2] = 2×[0.0010] = 2.0×10–3 M
pOH = –log[OH–] = –log[2.0×10–3] = 2.70
pH = 14.00 – pOH = 14.00 – 2.70 = 11.30
3. Indicate the stronger acid in each pair. Explain your reasoning in 5 words or less. For the stronger acid, write out the balanced reaction of the acid with water.
a. CF3COOH vs. CH3COOH
b. H4SiO4 vs. H3PO4
c. HCrO4– vs. HMnO4
a. CF3COOH vs. CH3COOH
CF3COOH because of the F electronegativity
CF3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + CF3COO–(aq)
b. H4SiO4 vs. H3PO4
H3PO4 because of more oxo-type O atoms
H3PO4(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + H2PO4–(aq)
c. HCrO4– vs. HMnO4
HMnO4 because of charge
HMnO4(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + MnO4–(aq)
4. Complete the following reactions and indicate which direction equilibrium will favor:
a. HBrO2(aq) + ClO2–(aq)
b. NH3(aq) + HF(aq)
a. HBrO2(aq) + ClO2–(aq) → ← HClO2(aq) + BrO2–(aq)
Equilibrium favors the side with the weaker acid, which is HBrO2 (electronegativity), so the reactants side is favored.
b. NH3(aq) + HF(aq) → ← NH4+(aq) + F–(aq)
Equilibrium favors the side with the weaker acid, which is HF (charge), so the reactants side is favored.
5. A 0.0010 M solution of fluoroacetic acid (CH2FCO2H, Ka = 2.6×10–3) was prepared. Find the pH.
CF3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + CF3COO–(aq)
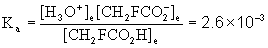
Initial 0.0010 0 0
Change –x +x +x
Equilibrium 0.0010 – x x x
Approximate? 0.0010/2.6×10–3 = 0.38: No
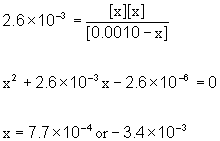
x = 7.7×10–4
[H3O+]e = 7.7×10–4 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log[7.7×10–4] = 3.11