 Exam 2B, Spring 2001
Exam 2B, Spring 2001 Exam 2B, Spring 2001
Exam 2B, Spring 20011. Complete and balance the following acid/base reactions. Label the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base for each reaction.
a. Ba(OH)2(aq) + HCl(aq)
b. C6H5COOH(aq) + H2O(l)
c. HClO4(aq) + H2O(l)
d. HN3(aq) + NH3(aq)
a. Ba(OH)2(aq) + 2 HCl(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Ba2+(aq) + 2 Cl–(aq)
Acid: HCl
Base: Ba(OH)2
Conjugate Acid: H2O
Conjugate Base: Cl–
b. C6H5COOH(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + C6H5COO–(aq)
Acid: C6H5COOH
Base: H2O
Conjugate Acid: H3O+
Conjugate Base: C6H5COO–
c. HClO4(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + ClO4–(aq)
Acid: HClO4
Base: H2O
Conjugate Acid: H3O+
Conjugate Base: ClO4–
d. HN3(aq) + NH3(aq) → ← NH4+(aq) + N3–(aq)
Acid: HN3
Base: NH3
Conjugate Acid: NH4+
Conjugate Base: N3–
2. Find the pH, pOH, [H3O+], and [OH–] for the following solutions at 25 °C.
a. 0.00017 M hydroiodic acid.
b. 2.4×10–5 M strontium hydroxide
c. A hydrofluoric acid solution with pH = 3.19
a. 0.0017 M hydroiodic acid.
HI(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + I–(aq)
[H3O+] = [HI] = 0.0017 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log[0.0017] = 2.77
[OH–] = Kw/[H3O+] = 1.0×10–14/0.0017 = 5.9×10–12 M
pOH = 14.00 – pH = 14.00 – 2.77 = 11.23
b. 2.4×10–5 M strontium hydroxide
Sr(OH)2(aq) → Sr2+(aq) + 2 OH–(aq)
[OH–] = 2×[Sr(OH)2] = 2×[2.4×10–5] = 4.8×10–5 M
pOH = –log[OH–] = –log[4.8×10–4] = 4.32
[H3O+] = Kw/[ OH–] = 1.0×10–14/4.8×10–5 = 2.1×10–10 M
pH = 14.00 – pOH = 14.00 – 4.32 = 9.68
c. A hydrofluoric acid solution with pH = 3.19
[H3O+] = 10–pH = 10–3.19 = 6.5×10–4 M
pOH = 14.00 – pH = 14.00 – 3.19 = 10.81
[OH–] = 10–pOH = 10–10.81 = 1.5×10–11 M
3. Indicate the stronger acid in each pair. Explain your reasoning in 5 words or less. For the stronger acid, write out the balanced reaction of the acid with water.
a. HNO3 vs. H2SeO4
b. H2Se vs. H2S
c. H3PO4 vs. HSeO3–
a. (HO)NO2 vs. (HO)2SeO2
HNO3 because N has greater electronegativity
HNO3(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + NO3–(aq)
b. H2Se vs. H2S
H2Se because of Se size
H2Se(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + HSe–(aq)
c. H3PO4 vs. HSeO4–
H3PO4 because of charge
H3PO4(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + H2PO4–(aq)
4. Find pKa for hyponitrous acid, H2N2O2, given that a 0.012 M solution is 0.27 % ionized.
H2N2O2(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + HN2O2–(aq)
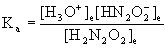
Initial 0.012 0 0
Change –x +x +x
Equilibrium 0.012 – x x x
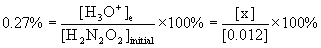
x = [H3O+]e = [HN2O2–]e = 3.2×10–5 M
[H2N2O2]e = 0.012 – x = 0.012 – 3.2×10–5 = 0.012 M
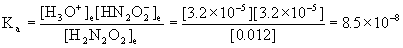
pKa = –logKa = –log(8.5×10–8) = 7.07
5. Find the pH of a 0.0055 M solution of hydrazinium ion, N2H5+.
N2H5+(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + N2H4(aq)
[H3O+]e [N2H5+]e [N2H6]e = 1.2×10–8
Initial 0.00055 0 0
Change –x +x +x
Equilibrium 0.00055 – x x x
Approximate? 0.0055/1.2×10–8 = 4.6×105: Yes
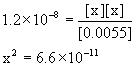
x = 8.1×10–6
[H3O+]e = 8.1×10–6 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log[8.1×10–6] = 5.09