 Exam 2B, Spring 2000
Exam 2B, Spring 2000 Exam 2B, Spring 2000
Exam 2B, Spring 20001. Complete and balance the following acid/base reactions. Label the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base for each reaction.
a. C6H5NH2(aq) + HBr(aq)
b. C2H5COOH(aq) + H2O(l)
c. (C2H5)3N(aq) + H2O(l)
d. HNO2(aq) + KOH(aq)
a. C6H5NH2(aq) + HBr(aq) → C6H5NH3+(aq) + Br–(aq)
Acid: HBr
Base: C6H5NH2
Conjugate Acid: C6H5NH3+
Conjugate Base: Br–
b. C2H5COOH(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + C2H5COO–(aq)
Acid: C2H5COOH
Base: H2O
Conjugate Acid: H3O+
Conjugate Base: C2H5COO–
c. (C2H5)3N(aq) + H2O(l) → ← (C2H5)3NH+(aq) + OH–(aq)
Acid: H2O
Base: (C2H5)3N
Conjugate Acid: (C2H5)3NH+
Conjugate Base: OH–
d. HNO2(aq) + KOH(aq) → H2O(l) + NO2–(aq) + K+(aq)
Acid: HNO2
Base: NaOH
Conjugate Acid: H2O
Conjugate Base: NO2–
2. Find the pH, pOH, [H3O+], and [OH–] for the following solutions at 25 °C.
a. 0.025 M perchloric acid.
b. 4.2×10–4 M calcium hydroxide
c. acetic acid solution with pH = 3.15
d. ammonia solution with pH = 10.32
e. 0.00056 M sodium hydroxide
a. 0.025 M perchloric acid.
HClO4(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + ClO4–(aq)
[H3O+] = [HClO4] = 0.025 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log[0.025] = 1.60
[OH–] = Kw/[H3O+] = 1.0×10–14/0.025 = 4.0×10–13 M
pOH = 14.00 – pH = 14.00 – 1.60 = 12.40
b. 4.2×10–4 M calcium hydroxide
Ca(OH)2(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + 2 OH–(aq)
[OH–] = 2×[Ca(OH)2] = 2×[4.2×10–4] = 8.4×10–4 M
pOH = –log[OH–] = –log[8.4×10–4] = 3.08
[H3O+] = Kw/[ OH–] = 1.0×10–14/8.4×10–4 = 1.2×10–11 M
pH = 14.00 – pOH = 14.00 – 3.08 = 10.92
c. acetic acid solution with pH = 3.15
[H3O+] = 10–pH = 10–3.15 = 7.1×10–4 M
pOH = 14.00 – pH = 14.00 – 3.15 = 10.85
[OH–] = 10–pOH = 10–10.85 = 1.4×10–11 M
d. ammonia solution with pH = 10.32
[H3O+] = 10–pH = 10–10.32 = 4.8×10–11 M
pOH = 14.00 – pH = 14.00 – 10.32 = 3.68
[OH–] = 10–pOH = 10–3.68 = 2.1×10–4 M
e. 0.00056 M sodium hydroxide
NaOH(aq) → Na+(aq) + OH–(aq)
[OH–] = [NaOH] = 5.6×10–4 M
pOH = –log[OH–] = –log[5.6×10–4] = 3.25
[H3O+] = Kw/[ OH–] = 1.0×10–14/2.8×10–4 = 1.8×10–11 M
pH = 14.00 – pOH = 14.00 – 3.25 = 10.75
3. Indicate the stronger acid in each pair. Explain your reasoning in 5 words or less.
a. HNO3 vs. H2SO4
b. CCl3COOH vs. CH3COOH
c. H2Se vs. H2Te
d. H2SeO4 vs. HSeO4–
a. (HO)NO2 vs. (HO)2SO2
HNO3 because N has greater electronegativity
b. CCl3COOH vs. CH3COOH
CCl3COOH because Cl has greater electronegativity
c. H2Se vs. H2Te
H2Te because of Te size
d. H2SeO4 vs. HSeO4–
H2SeO4 because of charge
4. Find the pH of a 0.072 M solution of hypobromous acid, HOBr. Show the appropriate chemical reaction required to solve the problem.
HOBr(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + OBr–(aq)
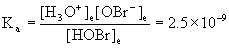
Initial 0.072 0 0
Change –x +x +x
Equilibrium 0.072 – x x x
Approximate? 0.072/2.5×9–11 = 3×107: Yes
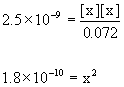
x = 1.3×10–5
[H3O+]e = 1.3×10–5 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log[1.3×10–5] = 4.89