 Exam 2A, Spring 2006
Exam 2A, Spring 2006 Exam 2A, Spring 2006
Exam 2A, Spring 20061. Complete and balance the following reactions:
a. solid calcium hydroxide plus aqueous hydrobromic acid
b. NH3(aq) + HN3(aq)
c. KOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq)
a. Ca(OH)2(s) + 2 HBr(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Ca2+(aq) + 2 Br–(aq)
b. NH3(aq) + HN3(aq) → ← NH4+(aq) + N3–(aq)
c. 2 KOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42–(aq)
2. Complete and balance the following reaction and identify the acid, the base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base:
bicarbonate ion + hydroxide ion
HCO3–(aq) + OH–(aq) → ← CO32–(aq) + H2O(l)
Acid: HCO3–
Base: OH–
Conjugate Acid: H2O
Conjugate Base: CO32–
3. Write the mass action expression for Kc for the following reactions.
a. N2(g) + H2(g) → ← NH3(g)
b. Br2(l) + H2O(l) → ← HOBr(aq) + HBr(aq)
a. Balance: N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → ← 2 NH3(g)
Kc = [NH3]e2 [N2]e[H2]e3
b. Already balanced: Br2(l) + H2O(l) → ← HOBr(aq) + HBr(aq)
Kc = [HOBr]e[HBr]e
4. Consider bicarbonate ion and hydrogen phosphate ion. Draw the Lewis dot structure for each species and identify the stronger acid in the pair. Briefly (5 words or less) justify your reasoning.
bicarbonate ion, HCO3–,
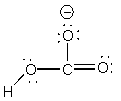 , stronger acid because less negative charge
, stronger acid because less negative charge
hydrogen phosphate ion, HPO42–,
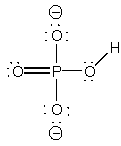 , weaker acid because more negative charge
, weaker acid because more negative charge
5. Write the reaction that occurs in water and calculate the pH and pOH of the following solutions:
a. 5.0×10–2 M perchloric acid.
b. 2.5×10–5 M magnesium hydroxide.
a. 5.0×10–2 M perchloric acid.
HClO4(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + ClO4–(aq)
[H3O+] = [HClO4] = 5.0×10–2 M
pH = –log([H3O+]) = –log(5.0×10–2) = 1.30
pOH = 14.00 – pH = 14.00 – 1.30 = 12.70
b. 2.5×10–5 M magnesium hydroxide.
Mg(OH)2(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH–(aq)
[OH–] = 2×[Mg(OH)2] = 2(2.5×10–5) = 5.0×10–5 M
pOH = –log([OH–]) = –log(5.0×10–5) = 4.30
pH = 14.00 – pOH = 14.00 – 4.30 = 9.70
6. Consider the reaction shown below, which has ΔH = –176.0 kJ/mol.
NH3(g) + HCl(g) → ← NH4Cl(s)
a. Which way will the reaction shift if ammonium chloride is added to the reaction? Explain.
b. Which way will the reaction shift if the temperature is raised? Explain.
NH3(g) + HCl(g) → ← NH4Cl(s) + heat (For an exothermic reaction, ΔH < 0, heat is a product)
a. Which way will the reaction shift if ammonium chloride is added to the reaction? Explain.
The reaction will not shift. The solid product concentration does not change so the equilibrium is not changed.
b. Which way will the reaction shift if the temperature is raised?
Raising the temperature adds heat so the reaction will shift towards reactancts to remove the added heat.
7. Estimate the equilibrium constant Kp for the following reaction.
Br2(l) + Cl2(g) → ← BrCl(g)
The following data has been reported:
Br2(l) → ← Br2(g) Kp = 0.28
Br2(g) + Cl2(g) → ← BrCl(g) Kp = 5.2
Use the Rule of Multiple Equilibria: if reactions are added, then the equilibrium constants are multiplied.
The two reactions with supplied equilibrium constants sum to give the target reaction so Kp for the target reaction = 0.28×5.2 =1.5
8. Estimate the pH of a 1.0 M solution of arsenous acid, H3AsO3. Ka = 6.6×10–10
H3AsO3(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + H2AsO3–(aq)
Ka = [H3O+]e[H2AsO3–]e [H3AsO3]e = 6.6×10–10
Initial 1.0 0 0
Change –x +x +x
Equilibrium 1.0 – x x x
Approximate? 1.0/6.6×10–10 = 1.5×109: yes
6.6×10–10 = x2/(1.0)
x2 = 6.6×10–10
x = [H3O+]e = 2.6×10–5 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log[2.6×10–5] = 4.59
Ka1 is so small that subsequent ionizations will not contribute to the pH.