 Exam 2A, Spring 1999
Exam 2A, Spring 1999 Exam 2A, Spring 1999
Exam 2A, Spring 19991. Identify the acid, base,conjugate acid, and conjugate base in the following reaction:
HCl(aq) + (CH3)NH2(aq) → (CH3)NH3+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
HCl(aq) + (CH3)NH2(aq) → (CH3)NH3+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
AcidBase Conjugate Acid Conjugate Base
2. Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in the following reaction:
Fe2+(aq) + 6 H2O(l) → ← Fe(H2O)62+(aq)
Fe2+(aq) + 6 H2O(l) → ← Fe(H2O)62+(aq)
AcidBase
3. Complete and balance the following reactions:
a. HI(aq) + H2O(l)
b. H2O2(aq) + H2O(l)
c. NH4+(aq) + H2PO4–(aq)
d. CN–(aq) + H2CO3(aq)
a. HI(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + I–(aq)
b. H2O2(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + HO2–(aq)
c. NH4+(aq) + H2PO4–(aq) → ← NH3(aq) + H3PO4(aq)
d. CN–(aq) + H2CO3(aq) → ← HCN(aq) + HCO3–(aq)
4. Find the pH of the following solutions at 25 °C:
a. 0.0056 M nitric acid
b. 1.00 g of hydrogen chloride dissolved in 1.00 L of water
c. 6.2×10–5 M solution of calcium hydroxide.
a. 0.0056 M nitric acid
HNO3(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + NO3–(aq)
[HNO3] = [H3O+]
pH = –log[H3O+] = -log(0.0056) = 2.25
b. 1.00 g of hydrogen chloride dissolved in 1.00 L of water
HCl(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
(1.00 g/(1.0 + 35.5) g/mol)/1.00 L = 0.0274 M HCl = [H3O+]
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log(0.0274) = 1.562
c. 6.2×10–5 M solution of calcium hydroxide.
Ca(OH)2(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + 2 OH–(aq)
[OH–] = 2×[Ca(OH)2] = 2×6.2×10–5 = 1.2×10–4 M
[H3O+] = Kw/[OH–] = 1.0×10–14/1.2×10–4 = 8.3×10–11 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log(8.3×10–11) = 10.08
5. Find the hydronium ion and hydroxide ion concentrations for the following solutions at 25 °C:
a. a perchloric acid solution with pH = 2.35
b. a solution prepared by dissolving 1.00 g of lithium hydroxide in 1.00 L of water
c. a 3.6×10–4 M solution of magnesium hydroxide
d. a sodium hydroxide solution with pOH = 4.1
a. a perchloric acid solution with pH = 2.35
[H3O+] = 10–pH = 10–2.35 = 4.5×10–3 M
[OH–] = Kw/[ H3O+] = 1.0×10–14/4.5×10–3 = 2.2×10–12 M
b. a solution prepared by dissolving 1.00 g of lithium hydroxide in 1.00 L of water
LiOH(aq) → Li+(aq) + OH–(aq)
[OH–] = [LiOH] = (1.00 g/(6.9 + 16.0 +1.0)g/mol)/1.00L = 0.0418 M
[H3O+] = Kw/[OH–] = 1.0×10–14/4.18×10–2 = 2.4×10–13 M
c. a 3.6×10–4 M solution of magnesium hydroxide
Mg(OH)2(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH–(aq)
[OH–] = 2×[Mg(OH)2] = 2×3.6×10–4 = 7.2×10–4 M
[H3O+] = Kw/[OH–] = 1.0×10–14/7.2×10–4 = 1.4×10–11 M
d. a sodium hydroxide solution with pOH = 4.1
[OH–] = 10–pOH = 10–4.1 = 8×10–5 M
pH = 14.00 – pOH = 14.00 – 4.1 = 9.9
[H3O+] = 10–pH = 10–9.9 = 1.×10–10 M
6. For each of the following, indicate the stronger acid.
a. H2S, H2Te
b. HClO3, HClO2
c. NH3, NH2–
a. H2S, H2Te
Te is the larger atom, implying a longer X-H bond, so H2Te is the stronger acid and H2S is the weaker acid
b. HClO3, HClO2
(HO)ClO2 has one more oxo oxygen than (HO)ClO; the higher electronegativity of the oxo-type oxygen atoms implies that HClO3 is the stronger acid and HClO2 is the weaker acid
c. NH3, NH2–
NH3 has a higher positive charge than NH2– so NH3 is the stronger acid and NH2– is the weaker acid (Note: both of these are bases so NH2– is the stronger base.)
7. A 0.0045 M solution of an acid was found to be 0.033% ionized at 25 °C. Find the pKa of the acid.
HA(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + A–(aq)
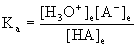
Initial 0.0045 0 0
Change –x +x +x
Equilibrium 0.0045 – x x x
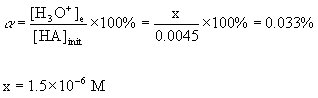
[H3O+]e = [A-]e = x = 1.5×10–6 M
[HA]e = 4.5×10–3 – x = 4.5×10–3 - 1.5×10–6 = 4.5×10–3 M
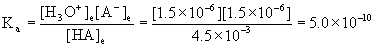
pKa = –logKa = –log(5.0×10–10) = 9.30
8. Find the pH of a 0.037 M solution of cyanic acid, HOCN, at 25 °C.
HOCN(aq) + H2O(l) → ← H3O+(aq) + OCN–(aq)
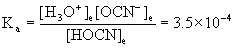
Initial 0.037 0 0
Change –x +x +x
Equilibrium 0.037 – x x x
0.037/3.5×10–4 = 110 so we can approximate:
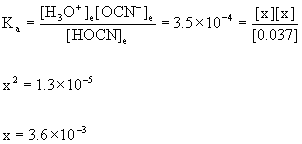
[H3O+]e= x = 3.6×10–3 M
pH = –log[H3O+] = –log(3.6×10–3) = 2.44