
CO(g) + H2O(g) → ← CO2(g) + H2(g)
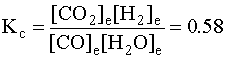
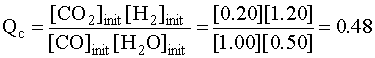
Since 0.48 < 0.58, the reaction proceeds to the products side
Initial 1.00 0.50 0.20 1.20
Change –x –x +x +x
Equilibrium 1.00 – x 0.50 – x 0.2 + x 1.20 + x
Plug the equilibrium expressions into the mass action expression and do the algebra:
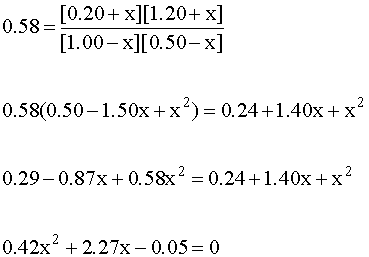
This requires the quadratic equation to solve:
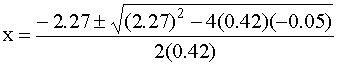
Solving gives x = 0.022 or x = –5.4
Only x = 0.022 makes chemical sense because x = –5.4 will lead to negative concentrations at equilibrium.
[CO]e = 1.00 – x = 1.00 – 0.022 = 0.98 M
[H2O]e = 0.50 – x = 0.50 – 0.022 = 0.48 M
[CO2]e = 0.20 + x = 0.20 + 0.022 = 0.22 M
[H2]e = 1.20 + x = 1.20 + 0.022 = 1.22 M